A recent research paper published by the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Liaoning University named ’Research on the Ecological Deconstruction of E-Cigarette Industrial Clusters in Shenzhen, China, and a Niche Analysis of Related Enterprises‘ on Sustainability Journal.
The study explains why Shenzhen is becoming the center of e-cigarette production and summarizes the reasons for the boom of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry.
Shenzhen E-Cigarette Industry Backgroud
According to data from the Electronic Cigarette Industry Committee of the China Electronics Chamber of Commerce, global sales of e-cigarettes reached USD 33 billion in 2019, a 106.25% increase compared with 2018 and a 14-fold increase compared to 2012. Global e-cigarette retail scale increased from USD 16.1 billion in 2016 to USD 56.9 billion in 2021. China’s e-cigarette market scale is also expanding, reaching CNY 116 billion in 2021, with most products exported overseas.
The results indicate that, after a long-term evolution, the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry has preliminarily built a business ecosystem with a unique structure. The developmental process is accompanied by the transformation of the development pattern from imitation to innovation and the enterprise populations have achieved coevolution through mutualistic symbiosis. In the area of technological innovation, niche-widening and -separation strategies are employed by the e-cigarette enterprises.
The above reasons explain the boom of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry and why Shenzhen is becoming the center of e-cigarette production.
In the early stage of the e-cigarette industry, Chinese non-tobacco companies first entered the e-cigarette field. In recent years, with the popularity and rapid development of new tobacco products worldwide, traditional tobacco companies such as the Yunnan China Tobacco Group and the Shanghai Tobacco Group have started e-cigarette businesses and launched a series of products.
At present, the global e-cigarette industry presents a pattern of the manufacturing center being located in China and the sales center being located in Europe and the United States. China is a major producer of e-cigarettes, with more than 90% of products in the global e-cigarette market being produced by private Chinese enterprises. Despite the continuous growth of e-cigarette production in China, e-cigarette consumption in China is relatively in a downturn. Of the total production, 90% is for export, and there are only a few influential Chinese e-cigarette brands.
Shenzhen, the center of Chinese e-cigarette production, has agglomerated thousands of e-cigarette enterprises and has developed a complete business ecosystem consisting of producers, suppliers, sellers, and competitors. E-cigarette manufacturers in adjacent cities are also in rapid development, driven by the prosperity of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry.
To explain the reasons for the prosperity of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry, we attempt to address the following topics in this research:
(i) The structure and evolutionary process of Shenzhen’s e-cigarette business ecosystem which includes e-cigarette enterprises and related organizations.
(ii) The developmental strategies adopted by the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry.
(iii) The relationships between enterprise populations on different parts of the industrial chain.
(iv) The development strategies for the survival and growth of e-cigarette enterprises in Shenzhen.
Business Ecosystem Structure of the Shenzhen E-Cigarette Industry
Figure 1 shows the detailed structure of the business ecosystem of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry. The ecosystem is mainly constituted of four components: core ecosystem, extended ecosystem, competitive species, and symbiotic species:
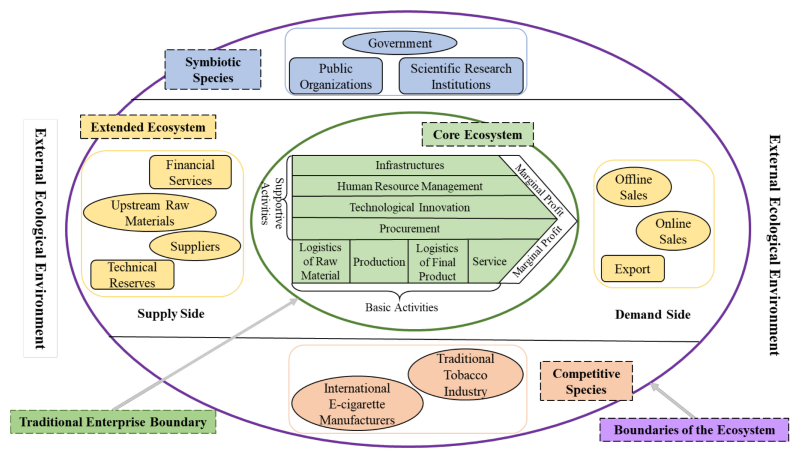
Core ecosystem: This part represents traditional e-cigarette enterprises which produce e-cigarette products and integrate with other parts of the business ecosystem. The boundaries here are equivalent to the boundaries of traditional e-cigarette enterprises. In the core ecosystem, innovation of internal activities is performed along the value chain to gain core competitiveness which is the foremost resource of the enterprises. For example, e-cigarette enterprises can obtain core technologies through technological innovation, or establish competitive advantages by strengthening marketing innovation.
Extended ecosystem: This part is constituted by the supply side and the demand side of e-cigarettes, which are critical for the business ecosystem. The supply side mainly includes
(1) manufacturers that provide upstream raw materials (battery cells, circuit boards, nicotine, etc.) to produce e-liquid, batteries, atomizers, and other accessories for e-cigarettes;
(2) laboratories built by enterprises and collaborative research institutes for technological support and reserves;
(3) suppliers of e-cigarette parts; and
(4) organizations that provide financial services. The demand side is the marketing channels of e-cigarette products, such as offline sales of dealers and agents, online sales on e-commerce platforms, and overseas exports to Europe, America, Southeast Asia, and Russia.
Competitive species: Competitive species represented by traditional tobacco enterprises and international e-cigarette manufacturers are potential threats to the core ecosystem of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry. Traditional tobacco enterprises have cultivated a large and fixed consumer population after years of tobacco sales. The price advantage, high consumer acceptance, and high market saturation of traditional tobacco products make it difficult for the market entrance and expansion of e-cigarette enterprises. In addition, Philip Morris International, British American Tobacco, Japan Tobacco, Imperial Tobacco, and other multinational tobacco companies have significantly developed in the e-cigarette area, making the international e-cigarette market increasingly competitive.
Symbiotic species: In the business ecosystem of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry, symbiotic species are crucial to the abiotic environment, so that they have a profound impact on the whole system. The symbiotic species include public organizations related to e-cigarettes (China Electronic Chamber of Commerce, Shenzhen E-cigarette Industry Association, etc.), scientific institutions (public health agencies, third party appraisal agencies, etc.), and government regulatory authorities (customs departments, tobacco departments, commodity inspection bureaus, etc.).
External ecological environment: The prosperity of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry is closely related to the unique external environment of Shenzhen: First, the complete industrial chain and well-developed hardware manufacturing industry have laid the foundation for the manufacturing of e-cigarette products. Second, numerous science and technology industrial parks in Shenzhen guarantee the technology reserve of the industry. Third, the improvement of intellectual property protection in China provides benefits for innovation, resulting in a significant increase in e-cigarette-related patents. Fourth, thousands of skilled grassroots staff in Shenzhen are high-quality labor resources that improve the frontline efficiency of e-cigarette production. Finally, endowed with a unique location and developed transportation, Shenzhen is convenient for the exporting of e-cigarette products.
Evolution Path of the Business Ecosystem
As an emerging industry, the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry is currently in rapid development, with a scale exceeding CNY hundreds of billion. According to the evolutionary stages of the business ecosystem, the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry is still in its expansion stage. Figure 2 shows its evolution path till now:
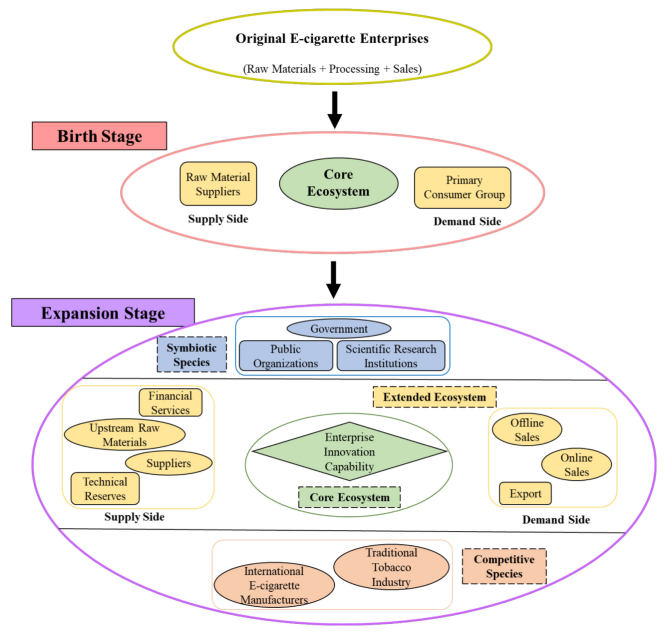
Birth stage: In the early stage of the development of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry, the scale of e-cigarette enterprises is small and the structure of the business ecosystem is simple. Enterprises in the core ecosystem have cultivated the first generation of consumer groups for e-cigarette products through production and sales. With the development of the industry, suppliers responsible for raw material manufacturing and demanders responsible for sales appear in the ecosystem, forming an initial industrial chain.
Expansion stage: In this stage, there is an expansion in the scale of enterprises and a gradual increase in the number of enterprises in the industry. Since enterprise saturation has not been reached within the industry, the dominant enterprise relationship is cooperation rather than competition, and there is a mutualistic symbiosis between e-cigarette enterprises.
Meanwhile, the industrial chain within the ecosystem is further improved: On the supply side, enterprises cooperate with research institutions or build their laboratories to carry out technological innovation to improve product quality and production efficiency. Simultaneously, a capital inflow of the ecosystem provides financial services for e-cigarette enterprises. In the core ecosystem, e-cigarette enterprises obtain core competency through technological innovation.
On the demand side, the diversification of sales channels further expands the consumer group of e-cigarette products. In addition, the accession of new members further complicates the structure of the business ecosystem: Public organizations such as the Electronic Cigarette Association are established through business alliances. Scientific research institutions are involved in the ecosystem through cooperation with e-cigarette enterprises. In this stage, the government actively intervenes in the e-cigarette industry and increases the supervision of products.
Public organizations, scientific research institutions, and the government together constitute symbiotic species of the business ecosystem. The development of the e-cigarette industry also attracts the participation of Chinese traditional tobacco companies, international tobacco companies, and others, which become competitive species of the business ecosystem.
Thus, a business ecosystem has been established gradually with the development of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry, and the ecosystem’s structure has transformed from being simple to being complex. During this process, the division of labor and the specialization of enterprises have emerged to achieve niche separation. A complete industrial chain, from raw material supply, to product processing, to sales, has been constructed.
The participation of symbiotic species, competitive species, and other members completes the structure of the business ecosystem. The above changes improve the stability of the business ecos
The Population Life History of the Shenzhen E-Cigarette Industry
The development history of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry is similar to the life history of plant populations. In the research on plant populations’ life history strategies, the stability of the environment is an important determinant for the choices made by plants. Similarly, when the surrounding environment changes, e-cigarette enterprises show adaptation to specific habitats under selection, in a similar manner to plant populations. Interactions and even coevolution also exist among the enterprises. Therefore, it is feasible to apply theories and methods of life history strategies and interspecies relationships to our research on the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry.
Development Strategies of the Industry—From the Perspective of Life History Strategies
The Shenzhen e-cigarette industry can be seen as a large population involving thousands of e-cigarette enterprises. As with plant populations, the industry employs different population life history strategies in different stages. Since the emergence of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry, the stress of its habitat is maintained at a low level, while the disturbance level in the habitat has decreased. Thus, the life history strategy of the industry has transformed from the ruderal strategy (R) to the competitive strategy (C) (Figure 3):
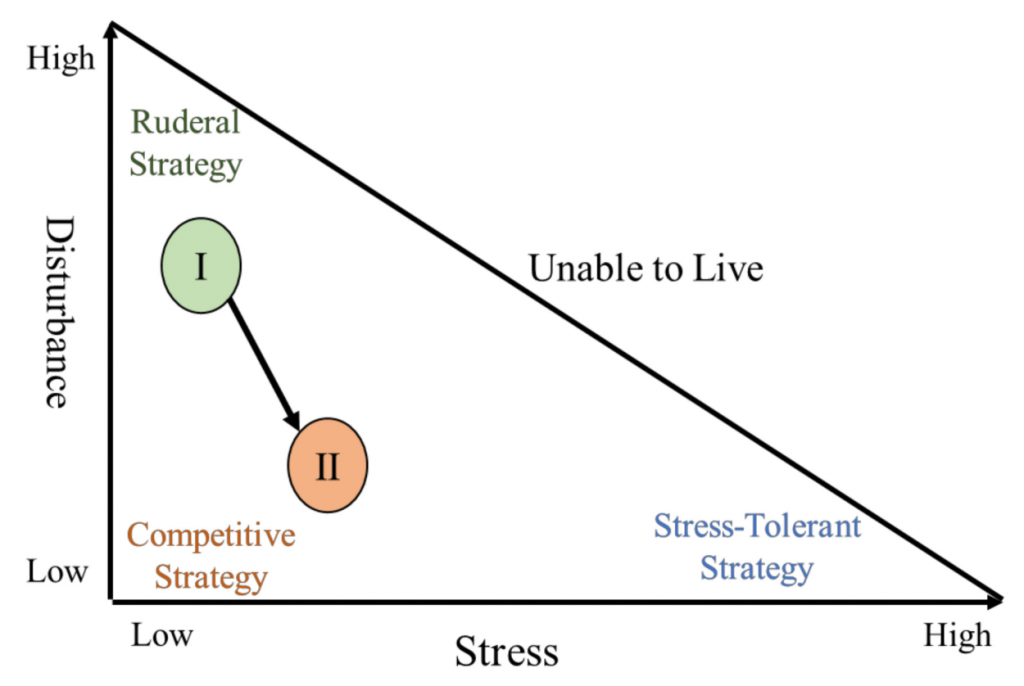
Stage I: This stage corresponds to the birth stage of the business ecosystem. As an emerging industry, there is a low level of environmental stress and substantial market resources for the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry. The popularity and scarcity of e-cigarettes cause products to sell out when exported overseas. However, high uncertainties exist for the capital, technology, labor, equipment, and raw materials required by the enterprise for production, as well as for the policies of the government, making the habitat unstable.
There are increasing numbers of new enterprises in this stage through “reproduction”, which means they are “genetically” similar: new e-cigarette enterprises are established by core employees who left original enterprises or new entrepreneurs through imitating the technologies, production, and sales of existing enterprises. These new enterprises resemble original enterprises in production, organization structure, and even management, showing the distinct phenomenon of “heredity”, in a similar manner to organisms. In this stage, e-cigarette enterprises are characterized by a small scale, simple product types, high natality, and high mortality, corresponding to the ruderal strategy (R).
Stage II: This stage corresponds to the expansion stage of the business ecosystem. The environmental stress is still moderate for the unsaturated market and abundant resources. Policies and standards of e-cigarette products are introduced by the government to strengthen the supervision of the industry and improve the market order. The volatility of the habitat is dramatically reduced because of the stabilization of the ecosystem structure. Therefore, enterprise mortality decreases gradually, and there is a large number of enterprises in the industry.
To maintain their competitiveness in the market, e-cigarette enterprises increase their investment in R&D, which promotes technological innovation in the industry and raises the barriers for new entrants. The “reproduction” of enterprises slows down due to industrial barriers, and several sizable enterprises emerge as a result of their technological advantages.
Meanwhile, there is diversification in both products and consumer populations, such that consumers can buy e-cigarettes by preference. In this stage, the life history strategy of the Shenzhen e-cigarette industry transforms from the ruderal strategy (R) to the competitive strategy (C), and the resource allocation priority shifts from “reproduction” to “growth”: The enterprises abandon stage I’s development pattern of imitation. Some of them focus on design and manufacturing for product differentiation, while others improve their brand influence through marketing strategies. More importantly, technological innovation is indispensable for e-cigarette enterprises to acquire core competitiveness.
by Yanmei Xu 1, ,Xia Song 1, Xiang Li 2, Ziqiang Wang 1 and Yanan Zhang 1 1. School of Economics and Management, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China 2. Business School, Liaoning University, Shenyang 110136, China Academic Editor: Ioannis Nikolaou Sustainability 2022, 14(9), 5606; https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095606


Average Rating